May is Employee Health Stay and Fitness Month — a perfect time to refocus on your personal wellness. As summer approaches, longer days and warmer weather open up even more opportunities to move your body, get outside, and recharge. Staying active during the summer months doesn’t have to mean training for a marathon or spending hours at the gym. Small, sustainable steps can make a big difference in how you feel both on and off the clock. Here are a few simple ways to stay fit and energized this summer.
Take Your Workouts Outside
Warmer temperatures and sunny days offer a natural invitation to get moving outdoors. Try trading the treadmill for a walk or jog around your neighborhood or a local park. Even a 20-minute brisk walk at lunchtime can boost your mood, increase focus, and help meet your daily fitness goals.
Stay Hydrated
Higher temperatures mean your body loses fluids more quickly. Dehydration can sneak up fast, especially during outdoor activities. Carry a reusable water bottle with you throughout the day and aim to drink consistently rather than waiting until you’re thirsty.
Break It Up
If you’re finding it hard to carve out an hour for a full workout, break it up into shorter sessions. A few 10-minute movement breaks — think stretching, bodyweight exercises, or a quick yoga flow — can add up over the course of a day and still deliver real benefits.
Make It Social
Physical activity doesn’t have to be a solo effort. Organizing a friendly walking group with coworkers or scheduling an active outing with friends can turn fitness into a fun, social event. Plus, you’re more likely to stick with it when it’s enjoyable.
Protect Yourself from the Sun
Don’t forget to apply sunscreen, wear a hat, and seek shade during peak sun hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.). Protecting your skin keeps you healthier in the long term — and helps you avoid uncomfortable sunburns that can derail your summer plans.
Listen to Your Body
Summer heat can be intense. Pay attention to how you’re feeling, and don’t push too hard during the hottest parts of the day. Early morning or evening workouts may be a better option when temperatures are cooler.
Small Steps Lead to Big Gains
You don’t have to overhaul your entire routine to see the benefits of staying active. Incorporating simple, mindful habits into your summer schedule can help you feel stronger, more energized, and better equipped to handle the demands of everyday life.
Employee Health and Fitness Month is a great reminder that your health is a priority — and every step you take matters.
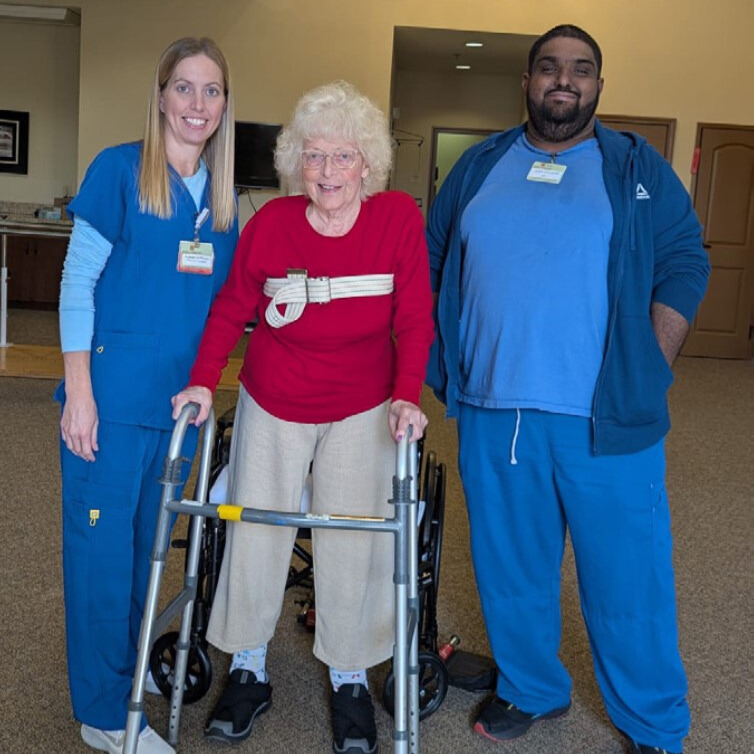




 Following a hospitalization for a tibial plateau fracture, Roy Cain arrived at The Madison on Marsh needing maximum assistance for all mobility and daily tasks. His journey toward recovery was challenging, requiring extensive therapy to rebuild strength and independence.
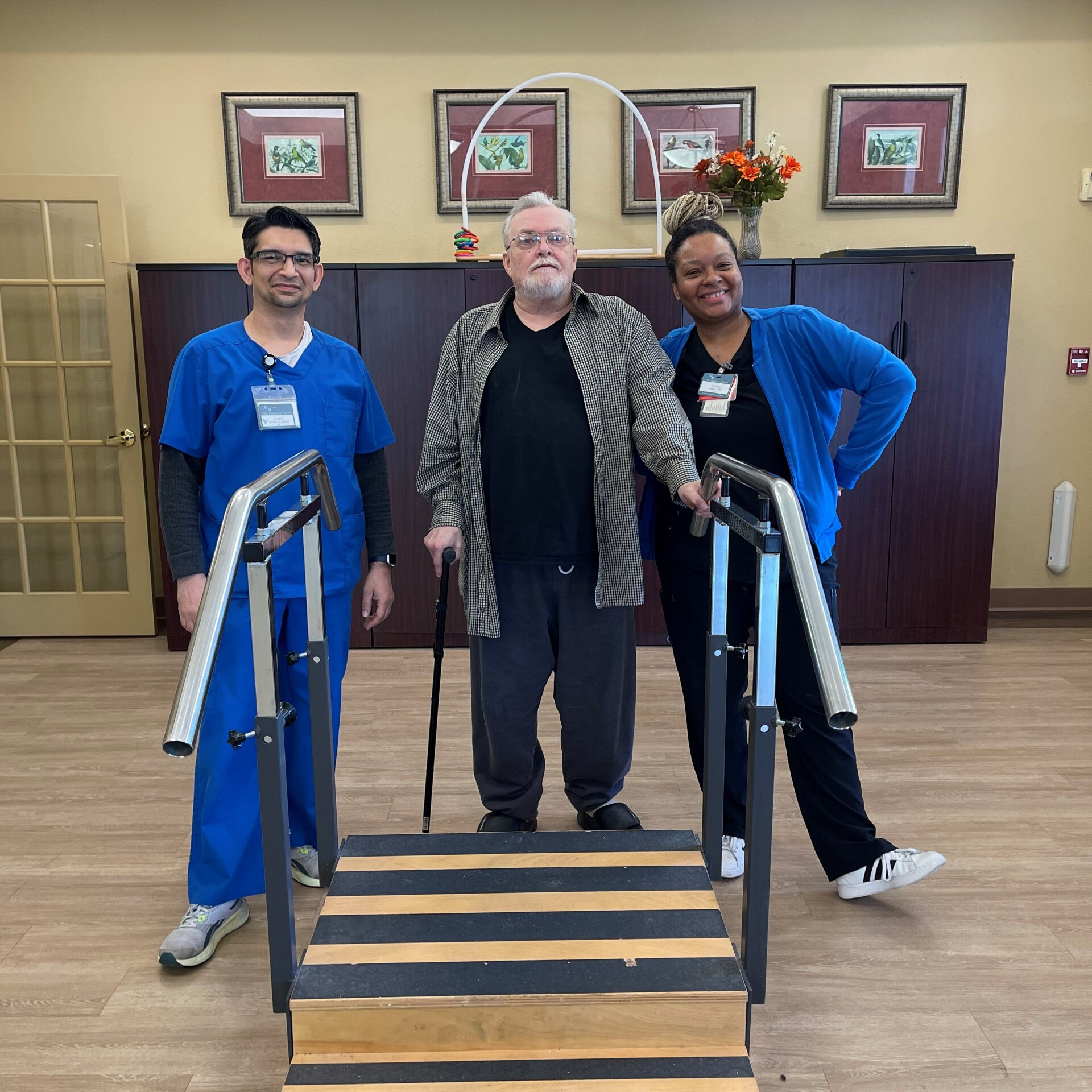
Following a hospitalization for a tibial plateau fracture, Roy Cain arrived at The Madison on Marsh needing maximum assistance for all mobility and daily tasks. His journey toward recovery was challenging, requiring extensive therapy to rebuild strength and independence.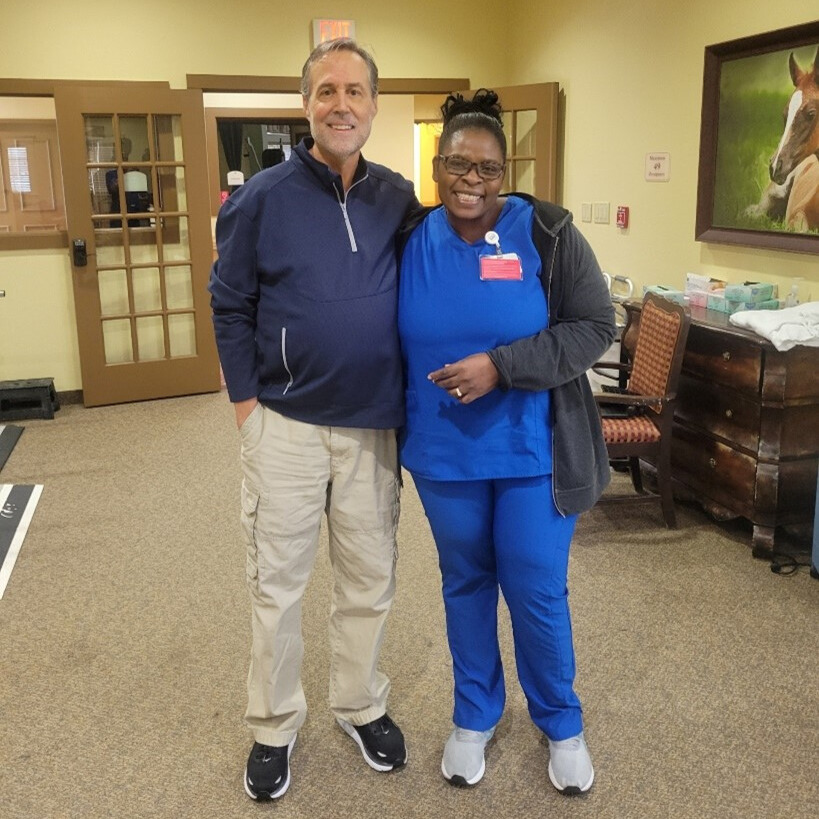 After being admitted to The Harrison at Heritage in August 2024, Mr. Cotton faced multiple health challenges, including altered mental status and mobility issues. Upon arrival, he was unable to perform basic self-care tasks or move independently.
After being admitted to The Harrison at Heritage in August 2024, Mr. Cotton faced multiple health challenges, including altered mental status and mobility issues. Upon arrival, he was unable to perform basic self-care tasks or move independently.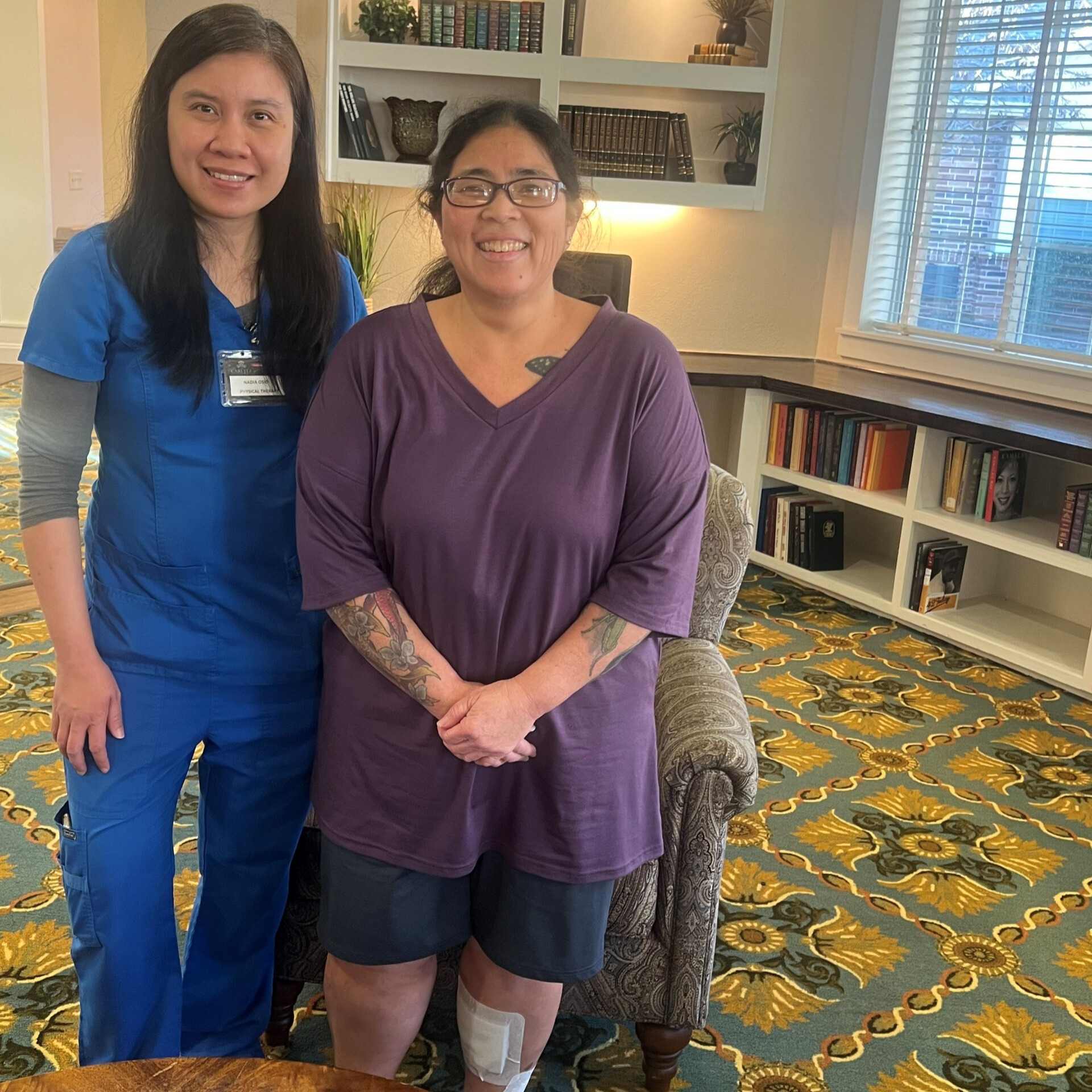 After sustaining multiple injuries in a motor vehicle accident, Ms. Koishigawa arrived at The Carlyle unable to bear weight on her right leg. She initially required significant assistance for mobility and daily tasks, but she remained determined to regain her independence.
After sustaining multiple injuries in a motor vehicle accident, Ms. Koishigawa arrived at The Carlyle unable to bear weight on her right leg. She initially required significant assistance for mobility and daily tasks, but she remained determined to regain her independence. At 81 years old, David Daniels faced multiple medical complications following hospitalization for generalized weakness and acute cystitis. Upon admission to Carrara, he required full assistance with mobility and daily activities.
At 81 years old, David Daniels faced multiple medical complications following hospitalization for generalized weakness and acute cystitis. Upon admission to Carrara, he required full assistance with mobility and daily activities.